

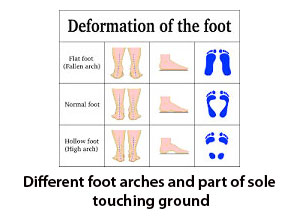
When we stand on bare foot whole sole does not touch the ground. Only heel lateral half of midfoot, fore foot and toes touches but medial half of midfoot remains off the ground. This happens because normal foot forms a longitudinal arch which is high on medial aspect and low on lateral aspect. This arch helps in balancing, shock absorbing and gait propagation. Shape and height of the arch is not constant in every individuals. If medial arch lost its height and whole sole touch the ground while weight bearing then it is called flat feet or Plano valgus feet. In Plano valgus foot height of medial arch is lost, heel shifts laterally and fore foot get abducted. If medial arch height becomes more than its normal range then only minimal portion of lateral border of mid foot sometimes even none touches the ground, heel shifts medially and for foot get adducted. This condition is called Cavus or Cavo-Varus feet.
Flat foot can be developmental or can also develop at adulthood who was otherwise having a nor arch of foot in early life. The second variant of flat foot is called adult acquired flat foot. It occurs due to insufficiency of tibialis posterior tendon function due to degeneration and tear or secondary to mid foot injury; Lisfranc’s fracture dislocation or rupture of spring ligament.
Developmental flat foot can be either flexible or rigid. Rigid variety develops due to abnormal bony bridge between hind foot tarsal bones. Either talocalcaneal coalition with a bony bridge between talus and calcaneum or calcaneonavicular coalition with a bony bridge between calcaneum and navicular bone. Due to this bony bridge normal growth of foot arch does not happen and flat foot develops which become obvious during adolescence. New born does not have foot arch. They developed it with their growth. It continues to develop till the age of 7-10 years of age. Any child still showing a flat arch after the age of 10 which can be re-created with manoeuvre is called flexible developmental flat foot.
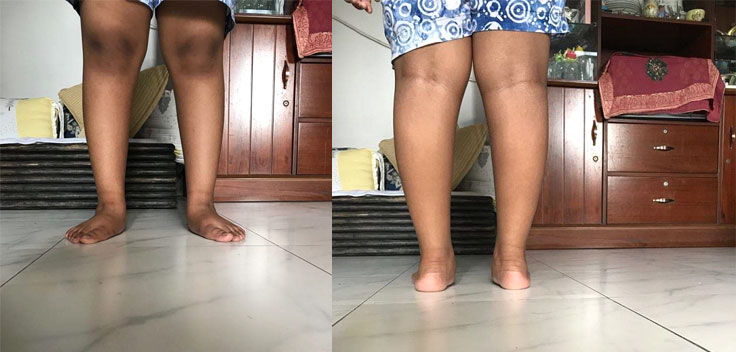
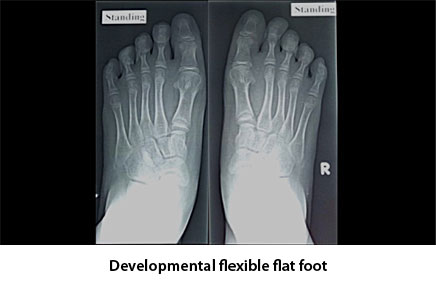
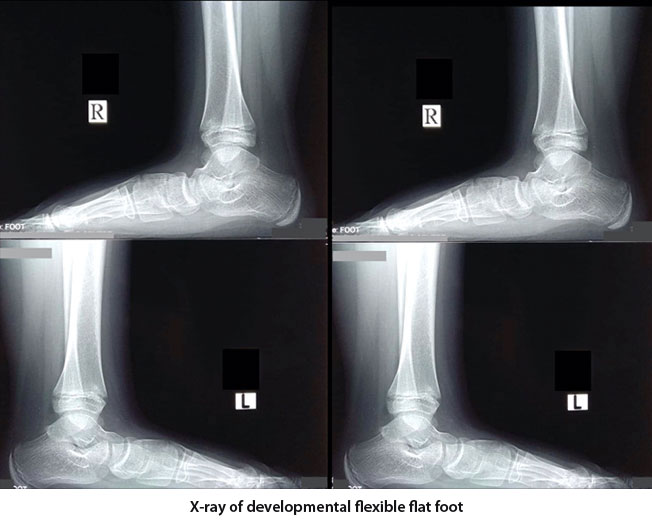
Every flat foot does not need active treatment. Many of the flexible flat foot never complains of any symptom till their late age and can perform all their activities like other normal child. Most of the time symptomatic flexible flat foot can do well with a insole which can correct and maintains the foot arch. Very few may need surgical correction. Developmental flat foot with very severe deformity may need early intervention with surgical correction of foot arch with different osteotomies. Symptomatic rigid flat foot requires correction of foot arch by arthrodesis of hind foot and mid foot joints, which includes subtaler, talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints and is called triple fusion.
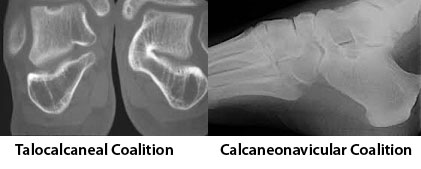
Investigation required for flexible flat foot is weight bearing x-ray of both feet in antero-posterior and lateral orthogonal view. Relationship between different foot bone can be established by measuring different angles. These angles are important for defining and grading the deformity. For rigid deformity x-ray may not be sufficient to diagnose a coalition. It may need both CT scan and MRI to identify a coalition.

Adult Acquired Flat Foot : Please see at tibialis posterior tendon dysfunction.